Golestan National Park
Golestan National Park: A Sanctuary of Breathtaking Biodiversity
Nestled in the northeastern corner of Iran, Golestan National Park stands as a testament to the country’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage. This vast and diverse protected area encompasses a wide range of ecosystems, from dense forests to arid landscapes, creating a haven for an incredible variety of flora and fauna.
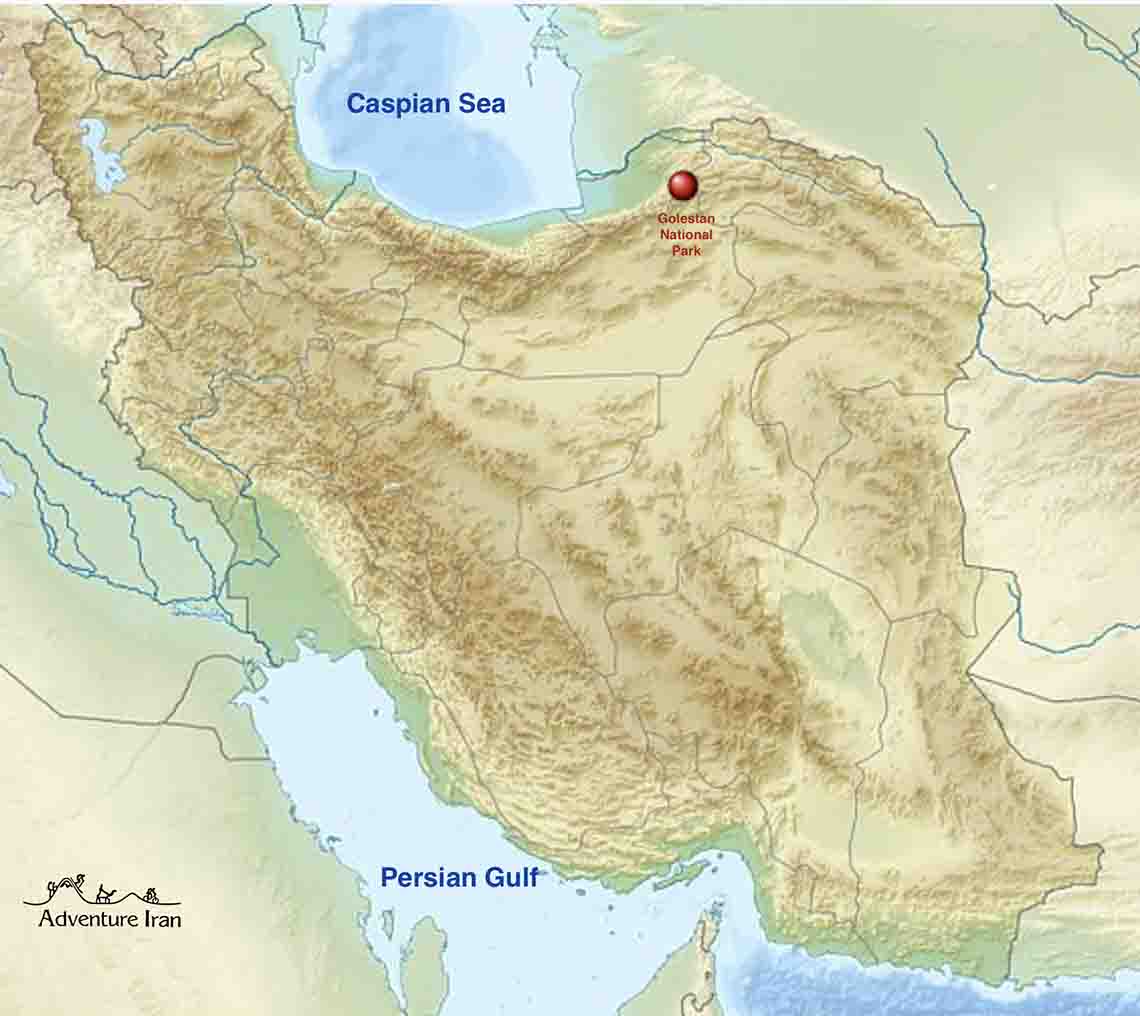
Golestan Biosphere Reserve is situated in Golestan province of Iran at the border to Turkmenistan. It belongs to the Caucaso-Iranian highlands and is situated in-between the sub-humid and semi-arid Caspian regions. The biosphere reserve represents three biomes: temperate rain forest, cold (continental) winter and semi-deserts and mixed mountain and highland systems. A vast variety of habitats can be found, such as closed forests, open woodlands and shrubs, mountain meadows, steppes, halophytic, hygrophilous and aquatic communities. Golestan is also designated as a national park.
Golestan offers a great ethnic diversity. The 26,000 inhabitants (2000) of the biosphere reserve are Turk, Persian and Kurdish. Their main activities consist in agriculture, animal husbandry, horticulture, industry, silk production and tourism. Adverse effects on the transition area come from traffic, overgrazing of rangelands and deforestation.
1. Introduction: Nature’s Masterpiece
A. Size and Location
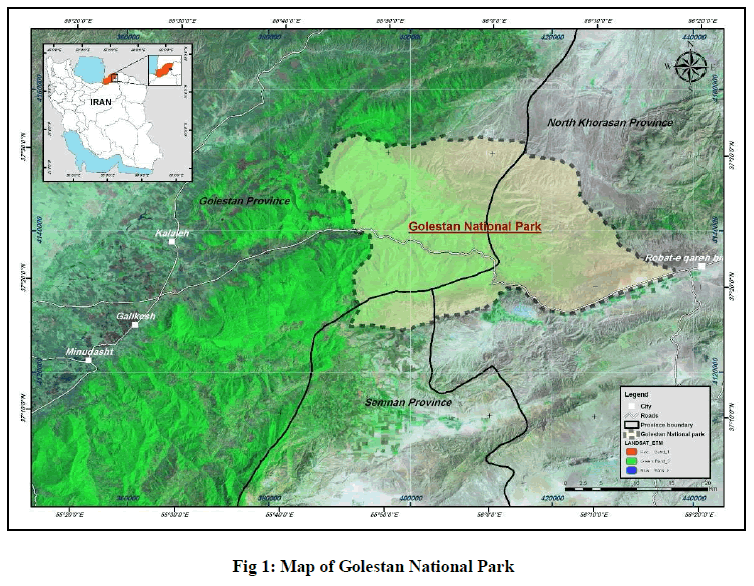
Golestan National Park, established in 1957, spans over 900,000 hectares, making it one of the largest national parks in Iran. Located in the Golestan Province, it encompasses a rich tapestry of landscapes.
B. UNESCO Biosphere Reserve
Recognizing its ecological significance, Golestan National Park was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve in 1976, underscoring its role in the conservation of biodiversity.
2. Biodiversity Hotspot: Flora and Fauna
A. Diverse Ecosystems
The park boasts an astonishing diversity of ecosystems, including temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, alpine meadows, and vast steppes. Each zone harbors a unique array of plant and animal species.
B. Rare and Endangered Species
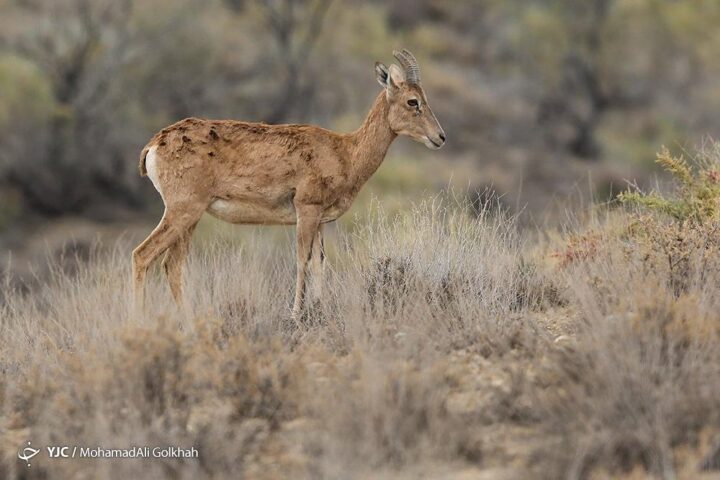
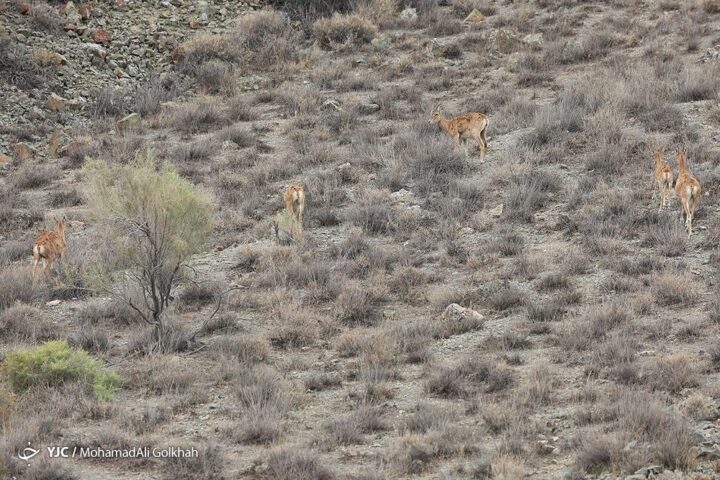
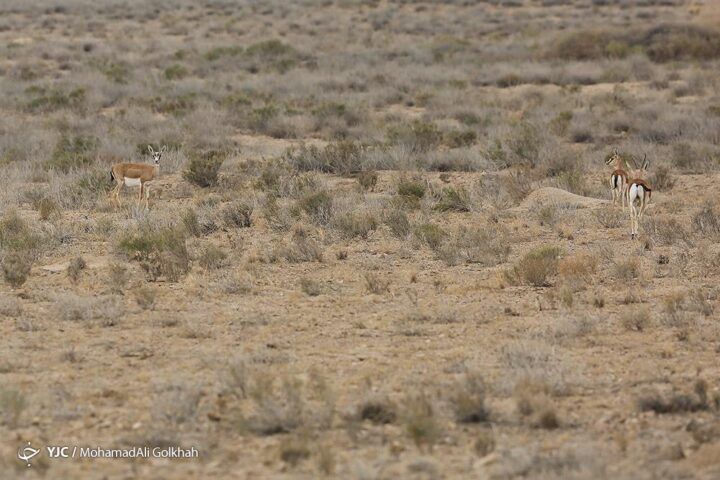
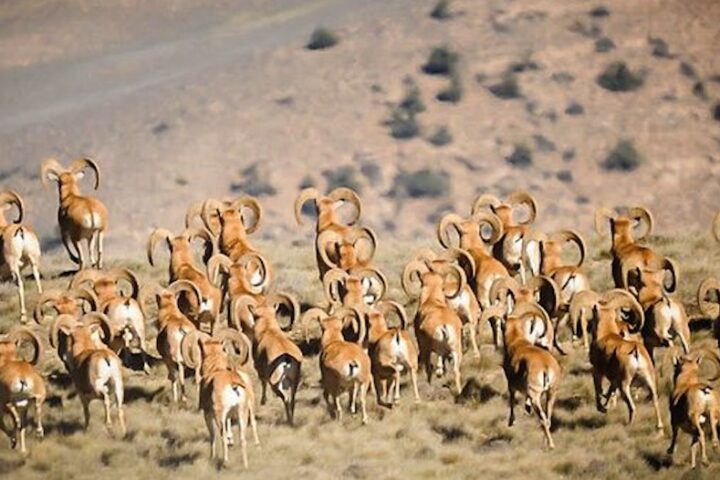
Golestan National Park is a refuge for several rare and endangered species, including the Persian leopard, Goitered gazelle, and the wild goat species, the Bezoar ibex.
3. Flora: A Botanical Paradise
A. Forests and Woodlands
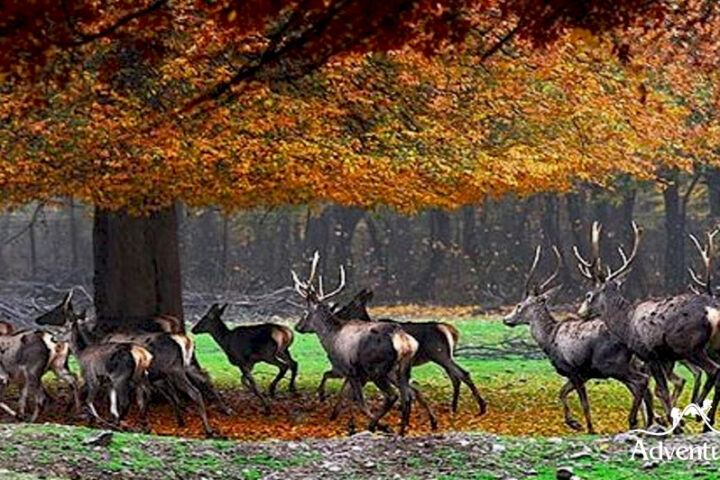
The park’s lush forests are dominated by deciduous and coniferous trees, creating a picturesque landscape. Oak, beech, and hornbeam trees are prevalent, while conifers such as fir and spruce add to the green canopy.
B. Alpine Meadows
As elevation increases, alpine meadows come into play, displaying a vibrant tapestry of wildflowers. These meadows are essential for the park’s herbivores and contribute to the overall biodiversity.
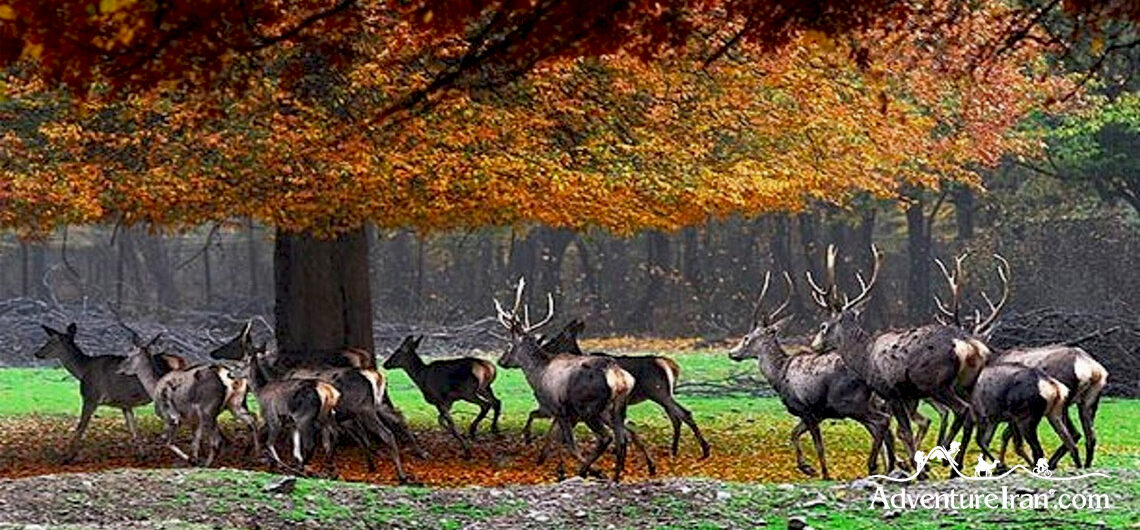
4. Fauna: A Symphony of Wildlife
A. Persian Leopard
Golestan National Park is a stronghold for the Persian leopard, a critically endangered subspecies. Conservation efforts aim to protect and increase the population of these elusive big cats.
B. Migratory Birds
The park serves as a vital stopover for migratory birds, with numerous species traversing its skies during their journeys. This has elevated the park’s status as a crucial bird-watching destination.
5. Human Interaction and Conservation
A. Indigenous Communities
Golestan National Park is home to several indigenous communities whose traditional practices coexist harmoniously with conservation efforts. Their sustainable lifestyles contribute to the park’s preservation.
B. Conservation Challenges
While the park has made strides in preserving its biodiversity, challenges such as poaching and habitat degradation persist. Ongoing conservation initiatives strive to address these challenges and ensure the park’s longevity.
6. Visitor Experience: Eco-Tourism and Adventure
A. Eco-Tourism Opportunities
Visitors to Golestan National Park can partake in eco-tourism activities, including hiking, bird-watching, and nature photography. The park’s diverse landscapes offer a captivating experience for nature enthusiasts.
B. Infrastructure and Facilities
The park provides well-maintained trails, camping areas, and educational centers to enhance the visitor experience while minimizing the ecological footprint.
7. Conclusion: Preserving Nature’s Legacy
Golestan National Park stands as a beacon of biodiversity conservation, where lush forests, alpine meadows, and elusive wildlife converge in a harmonious symphony. As Iran’s natural gem, it exemplifies the delicate balance between human and ecological needs, ensuring that future generations can marvel at the wonders of this living sanctuary.
Visitor Information:
- Location: Golestan National Park is situated in the Golestan Province of northeastern Iran.
- Access: The park is accessible by road, and various entry points cater to different zones within the park.
- Conservation Contribution: Visitors are encouraged to adhere to eco-friendly practices and support conservation initiatives to help protect the park’s delicate ecosystems.
Photography Travel to Turkmen Regions of Iran in Golestan Province








Comments